Testosterone is often linked with men, but it’s also important for women. This hormone affects energy, mood, muscle strength, and sex drive. When testosterone is low in women, it can lead to problems in both physical and emotional health. In this blog, we will talk about what low testosterone means for women, what causes it, the symptoms, and how to treat it.
Low Testosterone in Women: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Testosterone is a hormone mostly linked with men, but women need it too. It plays a big role in muscle strength, bone health, mood, and sex drive. As women get older, especially during menopause, their testosterone levels drop. This can lead to health problems. In this blog, we will explain what testosterone does for women, signs of low testosterone, what causes it, and how to treat it.
What is Testosterone and Why is it Important for Women?
Testosterone is a hormone made by the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. Even though it’s called a male hormone, it’s important for women’s health. Here’s how it helps:
- Muscle Strength: It helps build and keep muscle.
- Bone Health: It keeps bones strong.
- Mood: It helps balance emotions and keeps you happy.
- Sex Drive: It helps keep a healthy libido.
- Red Blood Cells: It helps make red blood cells that carry oxygen.
As women age, their testosterone levels naturally drop, especially during menopause. When levels drop too low, it can cause many health problems.
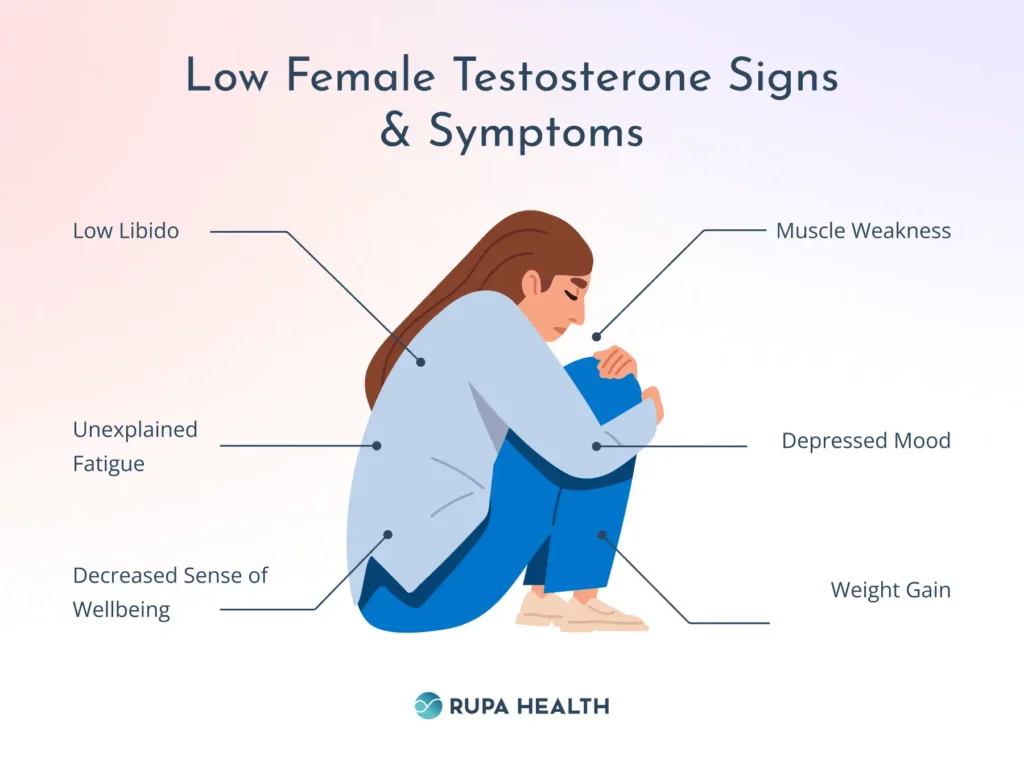
Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Women
Low testosterone in women affects them in many ways. These signs can show in your body, mood, and mind.
1. Tiredness and Low Energy
One of the most common signs is feeling tired all the time. Even after sleeping, you may feel drained and low on energy. This can make it hard to get things done during the day.
2. Low Libido
Testosterone is important for sexual desire. When it drops, many women notice a decrease in libido. This can affect intimacy and relationships. Women may lose interest in sex or find it less enjoyable.
3. Mood Swings and Depression
Low testosterone in women affects their emotions. It can cause mood swings, irritability, and sadness. Some women may feel anxious or depressed, or find it hard to stay positive.
4. Muscle Weakness
Testosterone helps keep muscles strong. When levels fall, muscles may feel weaker. You might find it harder to do simple tasks like lifting or carrying things.
5. Weight Gain
Weight gain, especially around the belly, is another common sign. Testosterone helps control fat in the body. When levels fall, fat may build up, making it harder to keep a healthy weight.
6. Brain Fog and Memory Problems
Low testosterone in women can make it hard to focus or remember things. You may feel forgetful or distracted. This can make everyday tasks harder.
What Causes Low Testosterone in Women?

There are many reasons for low testosterone in women, including aging, health problems, lifestyle choices, and stress.
1. Aging and Menopause
As women get older, their testosterone naturally drops. This is especially true during and after menopause, when the ovaries produce less testosterone. This drop can cause signs like tiredness, low libido, and mood changes.
2. Medical Conditions
Certain health problems can lower testosterone. For example, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can cause hormone imbalances. Conditions like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome can also lower testosterone levels.
3. Stress and High Cortisol Levels
Stress lowers testosterone. When stressed, the body makes cortisol, a hormone that can block testosterone production. Chronic stress can lead to mood changes and tiredness.
4. Poor Diet and Lifestyle Choices
A poor diet and lack of exercise can lower testosterone. Eating too much processed food and not exercising can affect hormone production. Regular exercise, especially strength training, helps boost testosterone.
5. Medications
Some medications, like birth control pills, antidepressants, and corticosteroids, can lower testosterone in women.
How to Boost Testosterone Naturally
There are ways to naturally boost testosterone. A good diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help.
1. Eat a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet is important for hormone health. Foods like avocados, fatty fish, and olive oil help boost testosterone. Eating zinc-rich foods like spinach and lean meats also helps. Vitamin D from eggs and sunlight is key. Limit processed foods and sugary snacks.
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercise helps boost testosterone. Strength training (like weightlifting) and HIIT (high-intensity interval training) are especially effective. Cardio exercises, like walking or cycling, help reduce stress, which is important for keeping cortisol levels low.
3. Manage Stress
Managing stress is key for healthy testosterone levels. Too much stress raises cortisol, which lowers testosterone. Try relaxing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to help manage stress.
4. Sleep Well
Sleep is important for hormone health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Poor sleep can affect testosterone levels. Having a regular sleep routine and good sleep habits helps improve sleep.
Medical Treatments for Low Testosterone
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medical treatments may be needed. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is one option. HRT gives testosterone through gels, patches, or injections. However, it’s important to talk to a doctor about the benefits and risks of HRT.
In some cases, doctors may suggest medications to help the body make more testosterone, especially if low levels are due to menopause or other hormone problems.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you think you have low testosterone, see a doctor. A blood test can check your testosterone levels. The doctor will use the test results and your symptoms to help decide the best treatment for you.
Conclusion
Low testosterone in women affects many parts of life, from energy and mood to physical strength and mental focus. But it can be treated. Eating well, exercising, and managing stress can help raise testosterone. In some cases, hormone therapy may be needed. If you think your testosterone is low, talk to a doctor. Taking steps now can improve your health, energy, and mood.