What is Testosterone Therapy ?
Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, is a condition that affects many men, especially as they age. It can lead to a range of physical, emotional, and mental symptoms that significantly impact quality of life. While low testosterone is a common issue, it can be difficult to recognize, as symptoms often develop slowly over time. This article will help you understand the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and potential risks associated with low testosterone, including alternatives to testosterone therapy for men when to consult with a specialist.
1. Understand the Symptoms of Low Testosterone
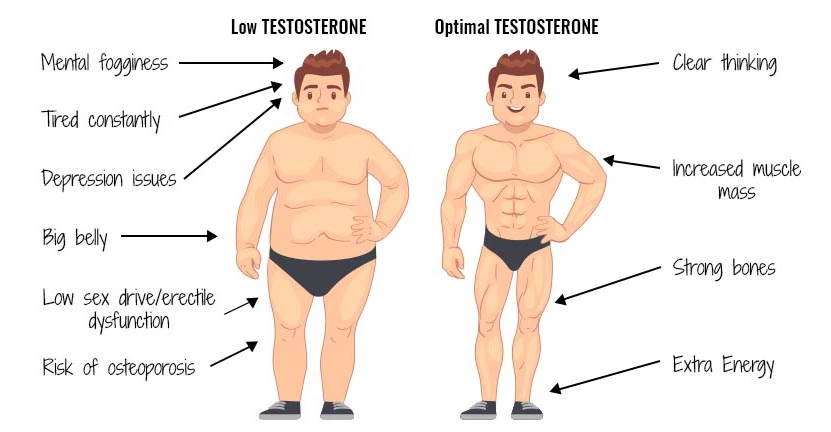
Testosterone is an important hormone for many things in the body, like muscles, bones, mood, and sex drive. When testosterone is low, men can feel different. The changes happen slowly, so it can be hard to know what’s causing them. Here are some signs of low testosterone:
- Fatigue: You may feel tired all the time, even after sleeping well. Men with low testosterone often feel drained and have no energy.
- Low Libido (Sex Drive): Testosterone controls sex drive. When it’s low, many men lose interest in sex and may have trouble getting or keeping an erection.
- Mood Changes: Low testosterone can cause mood swings. You may feel angry, sad, or anxious for no clear reason.
- Loss of Muscle Mass: Testosterone helps keep muscles strong. When it’s low, you may lose muscle and strength, even if you still exercise.
- Weight Gain: Low testosterone can slow metabolism, which can lead to weight gain, especially around the belly, even if you eat well and exercise.
- Loss of Bone Density: Testosterone helps keep bones strong. Low testosterone can make bones weaker and increase the risk of breaks.
- Cognitive Issues: Low testosterone can cause trouble with memory, focus, and mental clarity. You may feel forgetful or have trouble thinking clearly.
If these signs last for weeks or months, it’s a good idea to see your doctor. They can check your testosterone with a blood test.
2. Get Properly Diagnosed
To find out if you have low testosterone, your doctor will need to do a blood test. This test measures your testosterone levels. There are a few types of tests:
Blood Tests:
- Total Testosterone Test: This test checks the total testosterone in your blood. A normal level is usually between 300 ng/dL and 1,000 ng/dL. If your level is below 300 ng/dL, you may have low testosterone.
- Free Testosterone Test: This test checks the amount of testosterone that your body can actually use. It’s more accurate than the total testosterone test.
- Multiple Tests: Testosterone levels change during the day. Because of this, your doctor may want to test your levels several times to get the full picture.
Multiple Tests
Testosterone levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day, so a single test result might not be enough to make a diagnosis. Your doctor may ask for several tests, spaced out over a few days, to confirm whether your testosterone levels are consistently low.
3. Assessing Your Health and Medical History
Before starting testosterone therapy for men, your doctor will look at your overall health. Some health problems may make testosterone therapy less safe for you. Here are things your doctor will check:
- Prostate Health: Testosterone can affect the prostate. If you have prostate cancer or problems, testosterone therapy may make things worse. Your doctor may check your prostate before starting therapy.
- Heart Health: Testosterone therapy can increase the risk of heart problems, like heart attacks or strokes, especially for older men. Your doctor will check your heart health to make sure it’s safe for you to start therapy.
- Blood Clot Risks: Testosterone therapy for men can raise red blood cell levels. This may increase the risk of blood clots. If you’ve had blood clots before, testosterone therapy may not be safe for you.
- Sleep Apnea: If you have sleep apnea, testosterone therapy can make it worse. Sleep apnea is when your breathing stops and starts while you sleep. Your doctor may want to test you for this condition first.
4. Evaluating the Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy for men can help with many things. Some benefits include:
- Improved Sexual Function: Many men notice an increase in sex drive and better erectile function after starting testosterone therapy. It can also help with erectile dysfunction.
- Increased Energy: Testosterone therapy can help reduce tiredness. Men on therapy often feel more energetic and can do everyday tasks with more ease.
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone helps keep muscles strong. Therapy can help you gain muscle and strength, even if you continue to exercise.
- Better Mood and Mental Clarity: Testosterone therapy can improve mood. Many men feel less anxious or depressed and can think more clearly.
- Stronger Bones: Testosterone therapy can increase bone density and make bones stronger. This lowers the risk of fractures, especially for older men.
5. Considering the Risks and Side Effects
Testosterone therapy for men can have some risks and side effects. These include:
- Prostate Issues: Testosterone therapy can cause the prostate to grow. This can cause problems for men with prostate cancer. Regular checks are needed while on therapy.
- Heart Risks: Testosterone therapy may increase the risk of heart problems, especially for men with heart issues. Doctors monitor this risk carefully.
- Worsening Sleep Apnea: If you have sleep apnea, testosterone therapy may make it worse. Your doctor may want to do a sleep study to check this.
- Infertility: Testosterone therapy can lower sperm production, which may cause infertility. If you plan to have kids, talk to your doctor about other options.
- Skin Issues: Some men may get acne or oily skin from testosterone therapy. These side effects are usually mild but can be annoying.
6. Identify if Testosterone therapy is right for you ?
To know if testosterone therapy is right for you, it’s important to think about your symptoms, health, and talk to a doctor. Here’s how you can figure it out:
- Signs of Low Testosterone
- If you’re feeling tired all the time, losing muscle, gaining weight, or feeling sad or moody, your testosterone might be low. Testosterone therapy for men may help if these symptoms are due to low levels.
- You might also notice a drop in your sex drive or have trouble getting an erection. Testosterone therapy for men can sometimes help with these sexual health issues.
- Get Tested
- A doctor can do a blood test to check your testosterone levels. You might need a few tests on different days because your levels change throughout the day. These tests will help determine if testosterone therapy for men is necessary.
- Check Your Health
- Before starting testosterone therapy for men, your doctor will look at your overall health. If you have heart problems, sleep apnea, or prostate issues, it may affect whether testosterone therapy for men is safe for you.
- Think About Benefits
- Testosterone therapy for men can help you feel less tired, improve your mood, and increase your muscle strength. It can also help with sexual health and bone strength. These benefits make testosterone therapy for men a common choice for those with low levels.
- Consider Risks
- There are some risks with testosterone therapy for men, like heart problems, sleep issues, or acne. Some people may experience problems with fertility (difficulty having children). It’s important to discuss these risks before starting testosterone therapy for men.
- Talk to a Specialist
- It’s best to speak to a doctor who knows about hormone health, like an endocrinologist. They will help decide if testosterone therapy for men is a good choice for you.
7. Cost of Testosterone therapy for Men
The cost of testosterone therapy for men can vary depending on several factors, including location, the type of therapy, insurance coverage, and the healthcare provider. Here are some general price ranges:
- Injections:
- If you get testosterone injections, the cost can range from $30 to $150 per month without insurance.
- With insurance, the cost may be partially covered, reducing out-of-pocket expenses.
- Testosterone Gel:
- Testosterone gel can cost between $300 to $600 per month without insurance.
- Testosterone Patches:
- These can cost between $200 to $500 per month.
- Pellet Therapy:
- Pellets are implanted under the skin and usually cost between $500 to $1,000 for each procedure, which typically lasts for 3 to 6 months.
- Blood Tests:
- Blood tests to check testosterone levels may cost anywhere from $50 to $200, depending on the test and location.
It’s a good idea to check with your healthcare provider and insurance company to get a better idea of the exact cost for your situation.
8. Exploring Alternatives to Testosterone Therapy
Before starting testosterone therapy for men, you may want to try other ways to boost testosterone naturally. Here are some ideas:
- Exercise and Diet: Exercise, especially weight training, can help boost testosterone. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of protein, healthy fats, and vegetables can also help.
- Sleep Optimization: Getting enough sleep is important for healthy testosterone levels. Poor sleep can lower testosterone. Try to stick to a regular sleep schedule.
- Medications: Some medications, like clomiphene citrate or human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), can help your body make more testosterone naturally. These are alternatives to testosterone therapy for men.
9. Natural ways to boost testosterone
1. Exercise Regularly
- Strength Training: Lifting weights and doing resistance exercises can help increase testosterone levels. Compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are especially effective.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest periods can help boost testosterone.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet
- Protein: Eating enough protein can help maintain healthy testosterone levels. Include foods like eggs, lean meats, fish, and beans.
- Healthy Fats: Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil are important for testosterone production.
- Carbohydrates: Eating complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits can also help balance testosterone levels, especially when combined with exercise.
- Zinc-rich Foods: Zinc is essential for testosterone production. Include foods like oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, and spinach.
3. Get Enough Sleep
- Aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night. Poor sleep can lower testosterone levels, so improving your sleep quality can have a positive impact on your hormone levels.
4. Manage Stress
- Chronic stress leads to high levels of cortisol, a hormone that can lower testosterone. Try relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to reduce stress and keep cortisol levels in check.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Being overweight or obese can reduce testosterone levels. Losing excess fat, especially belly fat, can help improve testosterone production. Eating healthy and staying active are key factors in maintaining a healthy weight.
10. Consult with a Specialist

If you think you have low testosterone, it’s important to see a doctor who specializes in hormones. An endocrinologist or urologist can help figure out your symptoms and find the best treatment for you. Regular checkups will help ensure testosterone therapy for men is working and safe.
Conclusion
Testosterone therapy for men can improve many areas of life, such as mood, energy, muscle strength, and sexual health. It is important to understand both the benefits and risks. Testing and regular follow-ups are necessary to make sure testosterone therapy is the right choice for you. If you think you have low testosterone, talk to your doctor to discuss your options and what is best for your health.