Imagine a world where cars drive themselves, navigating bustling city streets and open highways without any human intervention. Autonomous vehicles are no longer just a concept from science fiction; they’re becoming a reality faster than many anticipated. With this exciting development comes an array of legal considerations and ethical dilemmas that society must grapple with.

Introduction to Autonomous Vehicles
As we inch closer to fully autonomous transportation, the question arises: How will our laws adapt? Additionally, what moral responsibilities do these intelligent machines hold? From federal regulations to state-specific rules, the landscape is complex and ever-evolving. Moreover, as we welcome self-driving cars into our lives, it’s essential to explore their broader impact on safety, behavior, and society itself.
Join us as we delve into the intricate web of legal frameworks surrounding autonomous vehicles while also examining their ethical implications. Understanding these aspects can help pave the way for responsible integration of this groundbreaking technology into our daily routines.
The Legal Framework for Autonomous Vehicles

The legal landscape for autonomous vehicles is complex and evolving. At the federal level, regulatory bodies like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) are developing guidelines to ensure safety and innovation coexist. These regulations aim to provide a framework that fosters technological advancement while addressing safety concerns.
State laws add another layer of complexity. Each state approaches autonomous vehicle legislation differently, resulting in a patchwork of rules. Some states have embraced these technologies with open arms, while others impose strict limitations.
Liability also poses significant challenges. Questions arise regarding who is responsible when an accident occurs involving an autonomous vehicle—manufacturers, software developers, or even passengers? Insurance requirements are adapting too, as traditional models may not adequately cover this new frontier of transportation technology. The legal implications are vast and will continue to evolve alongside advancements in autonomy.
A. Federal regulations
The landscape of autonomous vehicles is shaped significantly by federal regulations. These rules aim to ensure safety and foster innovation in this rapidly evolving sector.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) plays a pivotal role. It outlines guidelines for testing and deployment, emphasizing the need for thorough safety assessments before any vehicle hits the road.
Additionally, the U.
S. Department of Transportation has established frameworks that encourage collaboration between various stakeholders. This includes manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers working together to create uniform standards.
However, challenges remain. The rapid pace of technology often outstrips regulatory processes, creating gaps that could jeopardize public trust in these advanced systems. As lawmakers adapt to new developments, maintaining a balance between encouraging innovation and ensuring safety will be crucial moving forward.
B. State laws and regulations
State laws and regulations play a crucial role in the deployment of autonomous vehicles. Each state has the authority to create its own rules, which can lead to significant variations across the country.
Some states have embraced innovation by establishing comprehensive frameworks for testing and operating self-driving cars. California, for instance, requires companies to obtain permits before allowing their vehicles on public roads. This ensures a level of oversight that prioritizes safety.
Conversely, other states may lag behind or adopt restrictive measures that hinder development. These inconsistencies can create confusion among manufacturers and consumers alike.
In addition to operational guidelines, states also address issues like registration and licensing specific to autonomous technology. Understanding these local regulations is vital for stakeholders wanting to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape effectively.
C. Liability issues and insurance requirements
Liability issues surrounding autonomous vehicles present a complex landscape. As these self-driving machines become more prevalent, determining who is at fault in an accident can be challenging. Is it the manufacturer, the software developer, or the vehicle owner?
Insurance requirements also evolve alongside technology. Traditional auto insurance models may not suffice for vehicles that operate independently. New policies need to address unique risks associated with automated systems.
Insurers are beginning to tailor products specifically for autonomous vehicles. These policies might consider factors like AI performance and real-time data analytics when assessing risk.
Furthermore, as regulations develop, companies must navigate compliance while ensuring adequate coverage for their fleets. With advancements in technology come new responsibilities that both manufacturers and consumers will have to embrace together.
Ethical Implications of Autonomous Vehicles
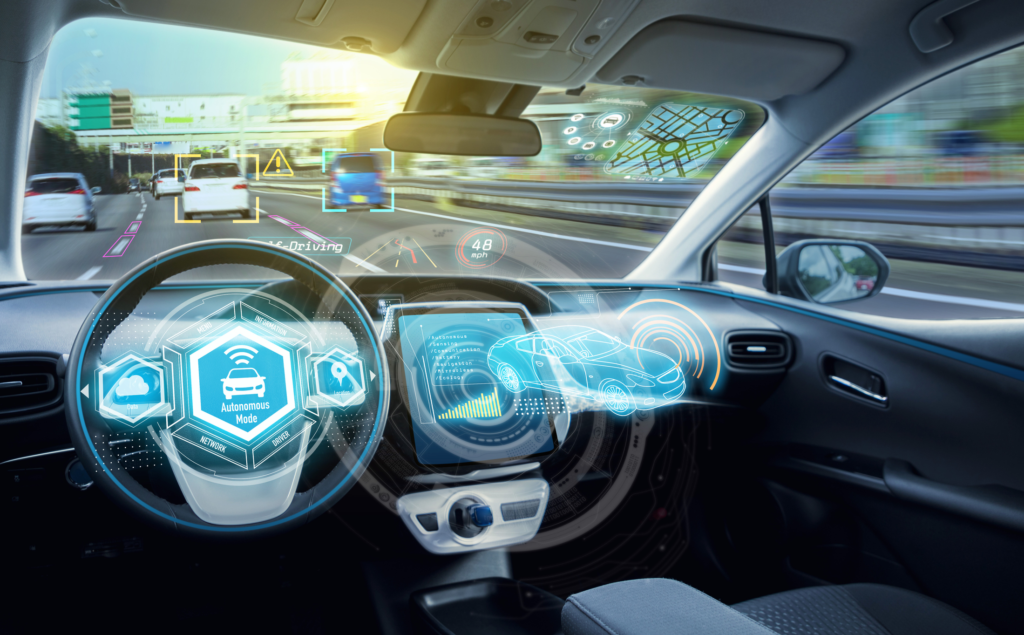

Autonomous vehicles bring a host of ethical dilemmas that society must confront. One well-known scenario is the trolley problem, where an AV must choose between two harmful outcomes in an emergency situation. Such decisions raise questions about how these machines prioritize lives and whether they should be programmed to value certain demographics over others.
Moreover, the introduction of self-driving cars can alter human behavior on the road. With reduced personal accountability, will drivers become more reckless? The reliance on technology could lead to complacency among passengers who may feel less compelled to pay attention.
The impact extends beyond individual choices; it reshapes societal norms around responsibility and safety. As we integrate autonomous vehicles into daily life, understanding their ethical implications becomes crucial for fostering trust in this transformative technology. These discussions engage not just engineers or lawmakers but every citizen affected by these advancements.
A. Trolley problem and other ethical dilemmas
The trolley problem presents a classic ethical dilemma, forcing us to choose between two unfortunate outcomes. In the context of autonomous vehicles, this philosophical conundrum becomes more pressing. Imagine an AV faced with a sudden decision: swerve and risk the lives of passengers or continue on its path and endanger pedestrians.
These scenarios push us to question how machines should make decisions that have life-and-death consequences. Should algorithms prioritize human lives over property? Or should they weigh the number of individuals involved?
As engineers program these vehicles, they grapple with not just technical challenges but moral ones too. The implications stretch beyond individual choices—shaping our understanding of responsibility in technology. How will society react when faced with such dilemmas on the road? The answers could redefine ethics itself as we integrate AVs into daily life.
B. Impact on society and human behavior
The arrival of autonomous vehicles is set to transform societal norms and human behavior in unexpected ways. With self-driving cars reducing the need for personal vehicle ownership, urban landscapes may shift dramatically. Public transport could experience a resurgence as people opt for shared autonomous rides.
In addition, our relationship with driving will evolve. Many individuals find joy or freedom in driving; losing that might alter how we engage with mobility altogether. This change could lead to new forms of social interaction as passengers connect differently during their rides.
Moreover, dependence on technology raises concerns about skills erosion. As more people rely on these vehicles, the art of navigation and driving may fade from collective memory. Consequently, society must grapple with both opportunities and challenges posed by this technological advancement while adapting behaviors around travel and connectivity in an increasingly automated world.
Challenges for Implementation
Implementing autonomous vehicles poses several formidable challenges. Technological hurdles remain at the forefront. Despite rapid advancements, ensuring safety and reliability is a complex task.
Public acceptance also plays a crucial role. Many people harbor concerns about sharing the road with driverless cars. Educating the public on their benefits could ease apprehensions.
Infrastructure adaptation cannot be overlooked either. Roads may require upgrades to accommodate these new technologies, including dedicated lanes or smart traffic signals.
Moreover, collaboration among various stakeholders—government entities, manufacturers, and tech companies—is essential yet often fraught with disagreement over regulations and standards.
Cybersecurity presents another significant challenge. Autonomous vehicles rely on intricate software systems that can be vulnerable to hacking or technical failures.
Ethical dilemmas complicate decision-making processes within programming algorithms. Balancing safety with human values raises many questions that still need answers before widespread implementation can occur.
Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The future of autonomous vehicles holds immense promise and possibility. As technology advances, we can expect significant improvements in safety, efficiency, and convenience.
Imagine a world where traffic congestion is minimized through smart routing. Vehicles will communicate with each other to avoid accidents and ensure smoother travel experiences.
Innovations like artificial intelligence will enhance decision-making processes within these vehicles. This means better navigation through complex urban environments.
Moreover, public acceptance is likely to grow as people witness the benefits firsthand. Trust in these technologies hinges on transparency, reliability, and consistent performance.
Infrastructure changes will also play a crucial role in supporting this evolution. Cities may adapt roadways and signage specifically for autonomous operation.
As we look ahead, it’s clear that the integration of autonomous vehicles into daily life could reshape our transportation landscape fundamentally.
Conclusion
The rise of autonomous vehicles marks a significant shift in transportation, bringing with it a host of legal and ethical considerations. As technology advances, the legal framework surrounding these self-driving cars must adapt to keep pace. Federal regulations provide foundational guidelines, while state laws create varied landscapes for testing and deployment.
Liability remains a complex issue. Who is responsible when an autonomous vehicle malfunctions? Insurance requirements are evolving too, as traditional models may not apply in this new context.
Ethically speaking, the implications are profound. The classic trolley problem illustrates just one dilemma engineers face when programming decision-making algorithms for AVs. These decisions could affect lives directly, making ethics an essential part of development discussions.
Moreover, society’s interaction with these vehicles will undoubtedly change human behavior on roads and beyond. Will people become more reliant on technology? How will trust be established?
Challenges abound in implementing autonomous vehicles widely—from technological hurdles to public acceptance and infrastructure readiness. Yet the future holds immense potential for safer roads and reduced traffic congestion if navigated thoughtfully.
As we move closer to integrating autonomous vehicles into daily life, attention must remain focused on both their legal frameworks and ethical responsibilities that accompany such innovations.
For more such content, keep visiting QAWire


